- Surveys & Programs
- Data & Tools
- Fast Facts
- News & Events
- Publications & Products
- About Us
NAEP Technical DocumentationSampling of Public Schools for the 2012 Long-Term Trend (LTT) Assessment
When designing each school sample, there are five objectives that underlie the process of determining the probability of selection for each school and how many students are to be sampled from each selected school. They are as follows:
- to meet the target student sample size for each age-specific sample
- to select an equal-probability sample of students
- to limit the number of students that are selected from a school;
- to ensure that the sample within a school does not include a very high percentage of the students in the school, unless all students are included
- to reduce the rate of sampling of small schools, in recognition of the greater cost and burden per student of conducting assessments in such schools
The goal in determining the school's measure of size (MOS) is to optimize across the last four objectives in terms of maintaining the accuracy of estimates and the cost effectiveness of the sample design.
Therefore, to meet the target student sample size objective and achieve a reasonable compromise among the other four objectives, the following algorithm was used to assign a measure of size to each school based on its age-specific enrollment as estimated from the sampling frame data.
The measures of size vary by enrollment size and within school target sample size. In general, very small schools were assigned an MOS that is one quarter of the target sample size of 64 students. The preliminary measures of size (MOSjs) for age j in school s were set as follows:
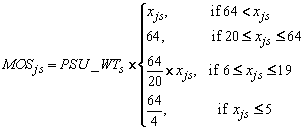
where xjs is the estimated age-specific enrollment for age j in school s, and PSU_WTs is the PSU weight for school s.
A school with more than 15 percent Black and Hispanic students and at least 10 Black or Hispanic students in the sample grade is in the high Black/Hispanic stratum for NAEP. The measures of size for schools in the high Black/Hispanic stratum are doubled to increase their chances of selection:

The next task in this development is to describe bj, the constant of proportionality for each age. It is a sampling parameter that, when multiplied with a school’s preliminary measure of size (Mjs), yields the school’s final measure of size. It is computed in such a way that, when used with the systematic sampling procedure, the target student sample size is achieved. For public schools, bj is 0.000050 for age 9, 0.000056 for age 13, and 0.000062 for age 17.
The final measure of size, Ejs, is defined as:
![]()
The quantity uj (the maximum number of times a school can be selected or “hits” allowed) in this formula is designed to put an upper bound on the burden for the sampled schools. For public schools, uj is 1.
In addition, new and newly-eligible schools were sampled from the new-school frame. The assigned measures of size for these schools
used the bj and uj values from the main school sample. The variable ![]() is the probability of selection of the district d into the new-school district sample.
is the probability of selection of the district d into the new-school district sample.
Schools were ordered within each jurisdiction using the serpentine sort described under the stratification of public schools. A systematic sample was then drawn using this serpentine sorted list and the measures of size. The numbers of public schools selected, including the original and new school sample were approximately 350, 375, and 400 for ages 9, 13, and 17, respectively.
The estimated number of age-eligible students was computed using a derived linear function of estimated grade enrollments. For 9-year-olds, the frame contained schools with a second, third, fourth, or fifth grade. Mjs(2), Mjs(3), Mjs(4), and Mjs(5) denote the estimated enrollments from the frame for the four grades respectively within each school s for age sample j . Fj(2), Fj(3), Fj(4), and Fj(5) denote the global proportion of students who were 9 years old (birth months January 2002 through December 2002) within each grade, Census region, and within public schools. These proportions were derived from the NAEP 2009 reading, mathematics, and science assessments. These values are shown in the table below for public schools. Age Distribution Fractions for Ages 9 and 13 describes how these proportions are computed.
| Census region | Fj(2) | Fj(3) | Fj(4) | Fj(5) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # Rounds to zero. NOTE: Detail may not sum to totals because of rounding. SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, National Center for Education Statistics, National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP), 2012 Long-Term Trend Assessment. |
|||||
| Northeast | 0.02 | 0.29 | 0.69 | # | 1.00 |
| Midwest | 0.02 | 0.41 | 0.56 | # | 1.00 |
| South | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.54 | # | 1.00 |
| West | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.69 | # | 1.00 |
The estimated number of age eligible students for the 9-year-olds component of the long-term trend (LTT) study for each school was computed as follows:
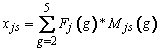
For 13-year-olds, the frame contained schools with a sixth, seventh, eighth, or ninth grade. Mjs(6), Mjs(7), Mjs(8), and Mjs(9) denote the estimated enrollments from the frame for the four grades respectively within each school s for age sample j. Gj(6), Gj(7), Gj(8), and Gj(9) denote the global proportion of students who were 13 years old (birth months January 1998 through December 1998) within each grade, Census region, and within public schools. These proportions were derived from the NAEP 2009 reading, mathematics, and science assessments. These values are shown in the table below for public schools. Age Distribution Fractions for Ages 9 and 13 describes how these proportions are computed.
| Census region | Gj(6) | Gj(7) | Gj(8) | Gj(9) | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # Rounds to zero. NOTE: Detail may not sum to totals because of rounding. SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, National Center for Education Statistics, National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP), 2012 Long-Term Trend Assessment. |
||||||
| Northeast | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.66 | # | 1.00 | |
| Midwest | 0.03 | 0.42 | 0.54 | # | 1.00 | |
| South | 0.07 | 0.40 | 0.52 | # | 0.99 | |
| West | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.67 | # | 1.00 | |
The estimated number of age eligible students for the 13-year-olds component of the LTT study for each school was computed as follows:
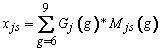
For the age 17 component, the frame contained schools with a ninth, tenth, eleventh, or twelfth grade. Mjs(9), Mjs(10), Mjs(11), and Mjs(12) denote the estimated enrollments from the frame for the four grades respectively within each school s for age sample j . Jj(9), Jj(10), Jj(11), and Jj(12) denote the global proportion of students born between October 1994 and September 1995 within each grade and Census region. The Current Population Survey (CPS) School Supplement (October 2009) was utilized to provide the proportions within each of ninth, tenth, eleventh, and twelfth grades for the age 17 component. The same table was used for both public and private schools since overall age distribution fractions were derived without differentiation of school enrollment by school type. The derivation of the Age Distribution Fractions for Age 17 describes how these proportions are computed.
| Census region | Jj(9) | Jj(10) | Jj(11) | Jj(12) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOTE: Detail may not sum to totals because of rounding. SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, National Center for Education Statistics, National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP), 2012 Long-Term Trend Assessment. |
|||||
| Northeast | 0.02 | 0.26 | 0.64 | 0.10 | 1.03 |
| Midwest | 0.04 | 0.32 | 0.63 | 0.06 | 1.06 |
| South | 0.09 | 0.30 | 0.59 | 0.06 | 1.03 |
| West | 0.02 | 0.22 | 0.67 | 0.04 | 0.95 |
The estimated number of age eligible students for the age 17 component of the LTT study for each school was computed as follows:
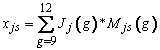
The SD/ELL Decision Tree Experiment was conducted as part of the NAEP 2012 assessement in 50 participating schools sampled for long-term trend (LTT) at ages 9 and 13. Schools eligible for the experiment were public schools with the modal grade (4 and 8) for the corresponding age 9 and 13 samples that have at least 25 age-eligible students. Eligible schools were sub-sampled from among the originally-sampled LTT age 9 and 13 schools using the sort order from the original sample design. A fixed-size sample of 55 schools from each age group was selected. The student sample size in the selected schools was increased to meet the sample size requirements for the experiment, as described in the student sampling section.
Last updated 26 February 2016 (GF)