- Surveys & Programs
- Data & Tools
- Fast Facts
- News & Events
- Publications & Products
- About Us
Table of Contents | Search Technical Documentation | References
NAEP Technical DocumentationCorrelations Among NAEP Subject Area Subscales
Two types of correlations are computed to assess the mathematical relationship between the final NAEP subject-area subscales. The first type is designated by NAEP as the conditional correlation coefficient and is directly derived from the population model parameters. The second type is designated by NAEP as the marginal correlation coefficient and follows from the imputation model. The marginal correlation coefficient reflects the correlation between the scales that are actually reported. The conditional correlation coefficient is a maximum likelihood point estimate of the correlation between the scales. Conditional correlations are conditional on student group membership (i.e., within-group). Marginal correlations include differences between student groups and are the overall correlation between the proficiency subscales. Because the reported scales are derived from the imputation model and some regression to the mean will occur, the marginal coefficients are generally somewhat lower than the conditional coefficients. Both coefficients provide a valid measure, but serve different purposes.
The conditional correlation coefficient is equal to the covariance between two subscales divided by the product of the standard deviations of each of the subscales. The covariances and standard deviations (i.e., the square root of the residual variance) are taken from the elements of ∑, the variance-covariance matrix whose rows and columns consist of latent cognitive traits (subscales), estimated as part of the multivariate latent regression of the population model. For more detailed information about these elements, see the Population Model section.
The marginal correlation coefficient is computed as the Pearson Correlation Coefficient between plausible values. For each plausible value, the correlations are computed and averaged using a Fisher
z transformation. Specifically, the correlations are transformed and averaged, and an inverse transformation is applied to the average. Fisher’s
z transformation is calculated as follows
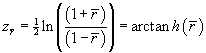
where 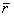 is the average marginal correlation and transforms the correlation to an approximately normal distribution. This transformation can also be used to compute standard errors.
is the average marginal correlation and transforms the correlation to an approximately normal distribution. This transformation can also be used to compute standard errors.
Marginal correlations are calculated for the nation and for each jurisdiction in state assessments. The state assessment estimates are summarized as the tenth, fiftieth, and ninetieth percentile correlations across jurisdictions in the assessment. Conditional correlation coefficients are reported for the nation only. Values for correlation coefficients can range from -1 to 1. The further this value is from zero, the stronger the relationship is considered to be, with a correlation coefficient of .90 or above demonstrating a very strong relationship.
| Subject | Assessment | Conditional correlations and residual variances of the subscales | Marginal correlations of the subscales | Select percentiles for correlations among the subscales for jurisdictions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 4 | Grade 8 | Grade 12 | ||||
| Arts | 2016 national assessment | § | § | § | § | § |
| 2008 national assessment | § | § | § | § | § | |
| Civics | 2018 national assessment | § | § | § | § | § |
| 2014 national assessment | § | § | § | § | § | |
| 2010 national assessment | § | § | § | § | § | |
| 2006 national assessment | § | § | § | § | § | |
| Economics | 2012 national assessment | R3 | R3 | † | † | † |
| 2006 national assessment | R3 | R3 | † | † | † | |
| Geography | 2018 national assessment | R3 | R3 | † | † | † |
| 2014 national assessment | R3 | R3 | † | † | † | |
| 2010 national assessment | R3 | R3 | † | † | † | |
| 2001 national assessment | R3 / R2 | R3 / R2 | † | † | † | |
| Mathematics | 2017 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † |
| 2015 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † | |
| 2013 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | |
| 2011 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † | |
| 2009 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | |
| 2007 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † | |
| 2005 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † | |
| 2003 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † | |
| 2000 national assessment | R3 / R2 | R3 / R2 | R3 / R2 | R3 / R2 | † | |
| Reading | 2017 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † |
| 2015 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † | |
| 2013 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | |
| 2011 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † | |
| 2009 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | |
| 2007 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † | |
| 2005 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † | |
| 2003 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † | |
| 2002 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † | |
| 2000 national assessment | R3 / R2 | R3 / R2 | † | † | † | |
| Science | 2015 combined national and state assessment | § | § | § | § | § |
| 2011 combined national and state assessment | § | § | § | § | § | |
| 2009 combined national and state assessment | § | § | § | § | § | |
| 2005 combined national and state assessment | R3 | R3 | R3 | R3 | † | |
| 2000 national assessment | R3 / R2 | R3 / R2 | R3 / R2 | R3 / R2 | † | |
| Technology and engineering literacy (TEL) | 2018 national assessment |
§ |
§ |
§ |
§ |
§ |
| 2014 national assessment |
§ |
§ |
§ |
§ |
§ | |
| U.S. history | 2018 national assessment | R3 | R3 | † | † | † |
| 2014 national assessment | R3 | R3 | † | † | † | |
| 2010 national assessment | R3 | R3 | † | † | † | |
| 2006 national assessment | R3 | R3 | † | † | † | |
| 2001 national assessment | R3 / R2 | R3 / R2 | † | † | † | |
| Writing | 2011 combined national and state assessment | § | § | § | § | § |
| 2007 combined national and state assessment | § | § | § | § | § | |
| 2002 combined national and state assessment | § | § | § | § | § | |
| Mathematics | 2012 long-term trend assessment | § | § | § | § | § |
| 2008 long-term trend assessment | § | § | § | § | § | |
| 2004 long-term trend assessment | § | § | § | § | § | |
| Reading | 2012 long-term trend assessment | § | § | § | § | § |
| 2008 long-term trend assessment | § | § | § | § | § | |
| 2004 long-term trend assessment | § | § | § | § | § | |
| † Not applicable. Conditional and marginal correlation tables are not created for the state assessment. The average marginal correlations and ranges of scales (that is, the average of all states participating in the state assessment) is calculated only for the state assessment. § Because the arts, civics, TEL, writing, and long-term trend assessment subjects use a univariate scale, tables for these subjects were not produced. Starting in 2009, science was also scaled univariately, and as a result tables for science were not produced. NOTE: Because preliminary analyses of students' writing performance in the 2017 NAEP writing assessments at grades 4 and 8 revealed potentially confounding factors in measuring performance, results will not be publicly reported. R2 is the non-accommodated reporting sample; R3 is the accommodated reporting sample. If sampled students are classified as students with disabilities (SD) or English learners (EL), and school officials, using NAEP guidelines, determine that they can meaningfully participate in the NAEP assessment with accommodation, those students are included in the NAEP assessment with accommodation along with other sampled students including SD/EL students who do not need accommodations. The R3 sample is more inclusive than the R2 sample type and excludes a smaller proportion of sampled students. The R3 sample is the only reporting sample used in NAEP after 2001. SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, National Center for Education Statistics, National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP), various years, 2000–2018 Assessments. | ||||||
Last updated 02 November 2022 (SK)